All About the Carnivorous Plant Aldrovanda Vesiculosa

Aldrovanda vesiculosa, also known as the Waterwheel Plant, is a fascinating carnivorous species that thrives in freshwater environments.
Unlike other carnivorous plants that trap insects on land, this plant specializes in capturing tiny aquatic invertebrates, making it unique and intriguing for plant enthusiasts.
Morphology and Feeding
From Venus Flytraps to Pitcher Plants – Shop the Best Carnivorous Plants and Kits!
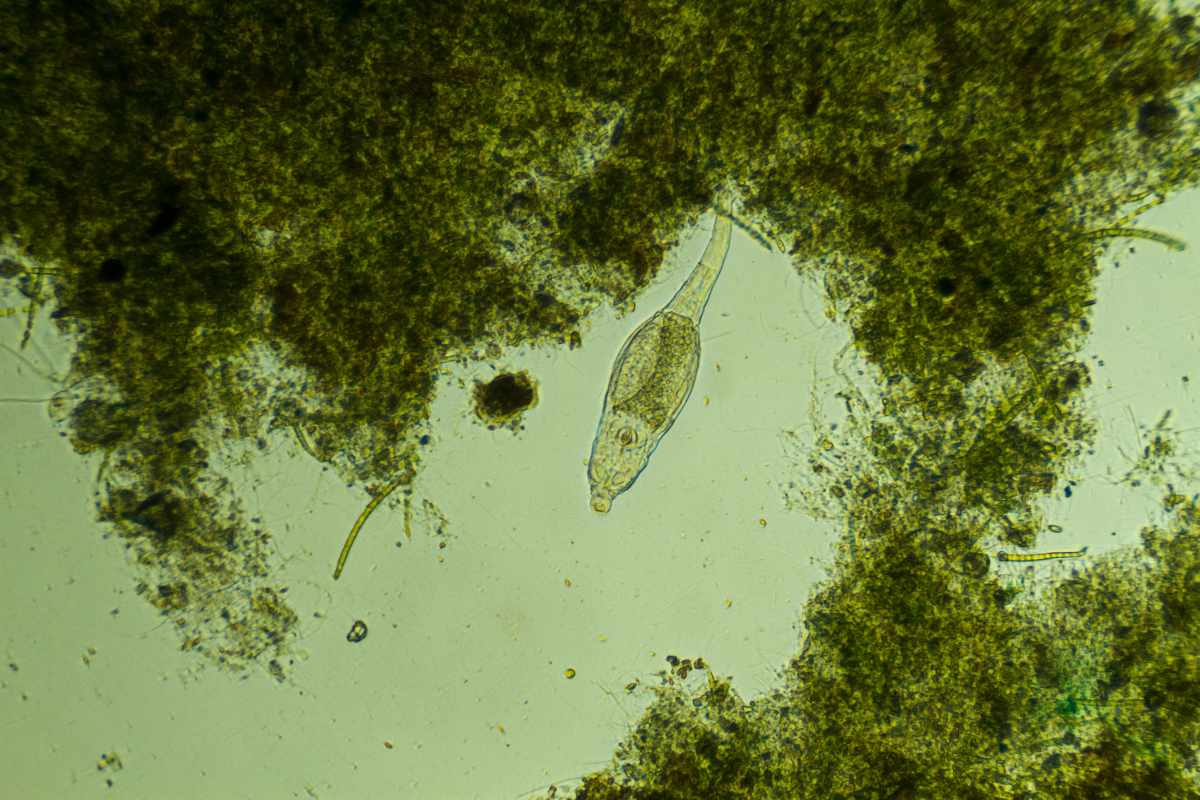
Aldrovanda vesiculosa is a floating plant with no true roots.
Its leaves form whorls along a central stem, with each leaf ending in small snap traps. These traps close rapidly when tiny prey, such as water fleas (Daphnia) or rotifers, touch the sensory hairs.
The plant then releases digestive enzymes to extract nutrients efficiently from its prey.
Understanding this feeding mechanism is essential for successful care, as it informs how the plant thrives in its natural environment.
Ideal Habitat Conditions
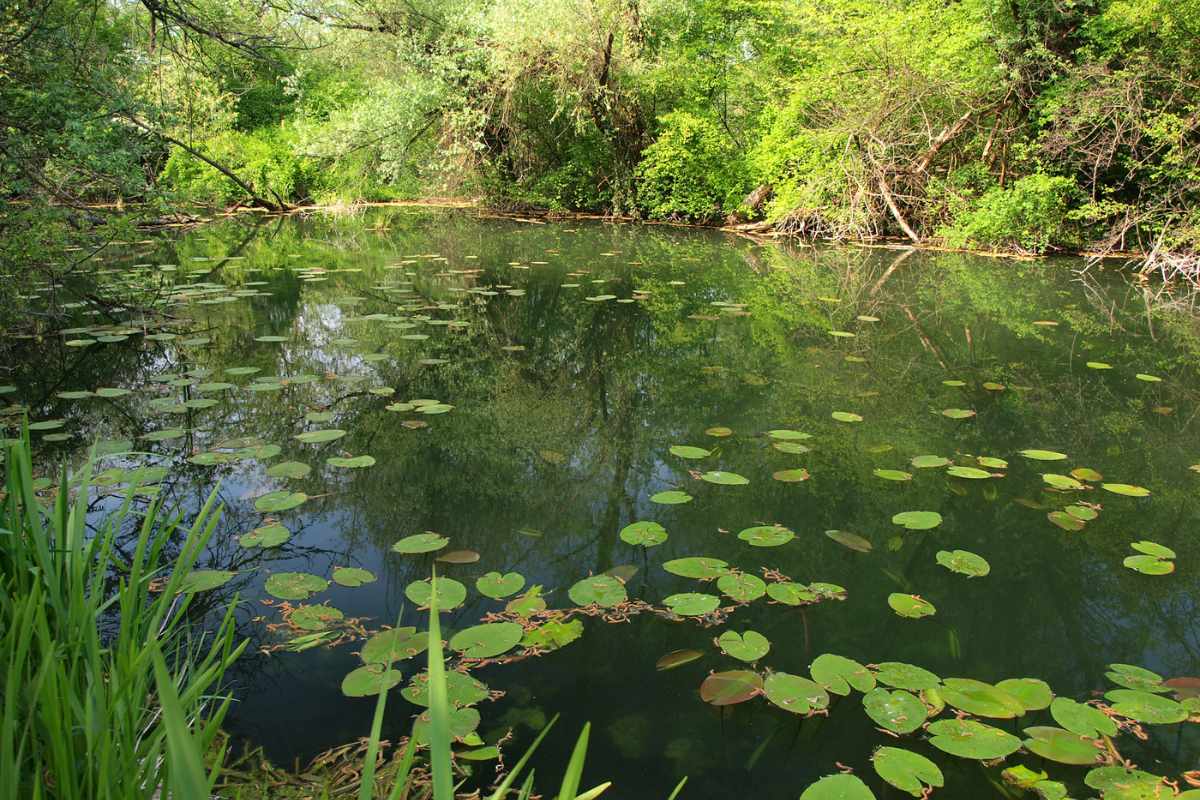

In the wild, Aldrovanda vesiculosa grows in clean, acidic, low-nutrient waters, often in ponds, slow-moving streams, or wetlands.
It is highly sensitive to water quality and requires low mineral content to remain healthy.
Maintaining similar conditions in cultivation is critical to prevent stress or dieback.
Temperature and Light Requirements
This species prefers moderate water temperatures, typically between 15–30°C (59–86°F).
It grows best under bright light, either direct sunlight or high-intensity artificial lighting, for at least 6 hours a day.
Light and temperature directly affect the plant’s growth rate and trap activity.
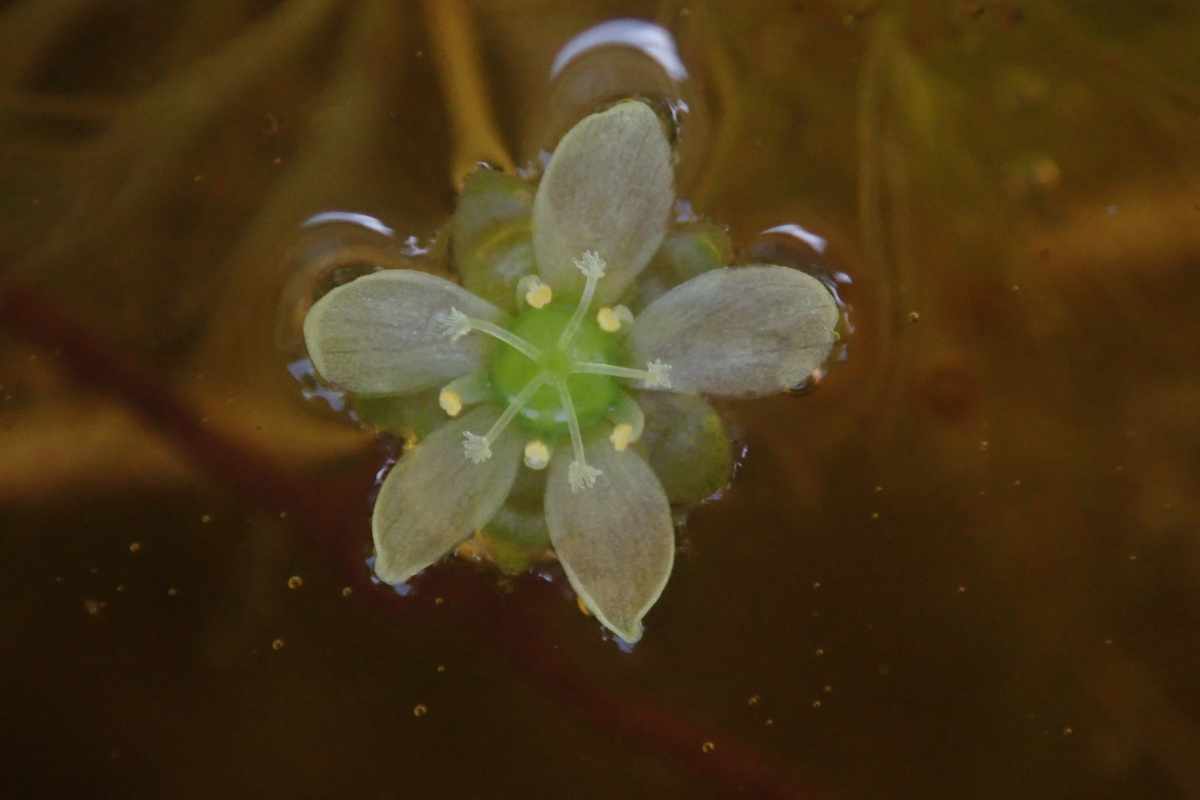
Propagation and Reproduction

Aldrovanda vesiculosa produces small white flowers that bloom briefly above the water surface, with pollination required for seed production.
In captivity, vegetative propagation is most common, achieved by fragmenting the plant.
While this allows for growth, it does not ensure genetic diversity, which is an important consideration for conservation.
Water and Substrate Guidelines

For cultivation:
Use distilled or rainwater to maintain low mineral content.
Avoid nutrient-rich substrates; the plant should float freely.
Do not use fertilizers or tap water with high mineral content, as these can harm the plant.
Maintaining proper water quality and keeping the plant free-floating are essential steps to ensure healthy growth.
Conservation Notes
Aldrovanda vesiculosa is endangered in many parts of the world due to habitat loss and water pollution.
Conserving its natural environment and replicating these conditions in cultivation are crucial for the survival of this species.
Aldrovanda vesiculosa is a delicate but rewarding plant to grow.
Providing clean water, adequate light, and the right temperature creates the conditions for healthy growth, active traps, and long-term success in cultivation.
Don’t forget to Subscribe to our Newsletter to receive amazing tips and tricks about Gardening and the FREE Ebook Green Living Strategies!
Did you find this post Useful or Inspiring? Save THIS PIN to your GARDENING Board on Pinterest! 😊

Once again, thank you for visiting our website!
We hope you've enjoyed exploring the content we've created for you.
Give yourself the chance to learn, get inspired, and have even more fun, keep browsing...
Last update on 2025-11-15 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API


More Gardening Tips 👇🏼👇🏼